Are you planning to build or restructure or venture into any healthcare venture in Afghanistan? Looking for information about the major healthcare players in government, and private hospitals that are available in Afghanistan? Are you looking to find out which part of the city is best to venture into or what all facilities are available and what should be planned for a new setup? In this article, Hospaccx Healthcare Consultancy has mapped all on major players in terms of medical facilities and the healthcare scenario of Afghanistan.
This is the superficial and macro level survey if you need a refined market and financial feasibility or any other study related to healthcare is required you can contact Hospaccx Healthcare business consulting Pvt. Ltd on Hospaccx.India@gmail.com or you can visit our website on https://hospaccxconsulting.com/
OVERVIEW OF THE COUNTRY
Afghanistan, formally known as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country in Central and South Asia. Following the collapse of the internationally recognized Islamic Republic of Afghanistan on August 15, 2021, it is currently administered by the Taliban. Afghanistan borders China, Iran, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The geography of Afghanistan is arid and mountainous; the Hindu Kush Mountains run northeast to southwest and divide the northern provinces from the rest of the country.
Health in Afghanistan remains poor but steadily improving. It has been negatively affected by the nation’s environmental issues and the decades of war. Afghanistan is a member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE
- Afghanistan has a population of 1 crore with a growth rate of 2.34% in the year 2023.
- Afghanistan’s population is equivalent to 5% of the total world population.
- Afghanistan ranks number 37 in the list of countries (and dependencies) by population.
- The population density in Afghanistan is 60 per Km2 (154 people per mi2).
- The total land area is 652,860 Km2 (252,071 sq. miles)
- 4 % of the population is urban.
- The median age in Afghanistan is 18.4 years.
- It has a birth rate of 3 births per 1000 population and a death rate of 13.7 deaths per 1000 population.
- The fertility rate in Afghanistan was 33 children born per woman and the infant mortality rate is 66.3 deaths per 1,000 live births.
- The sex ratio in Afghanistan is 05 males to females at birth.
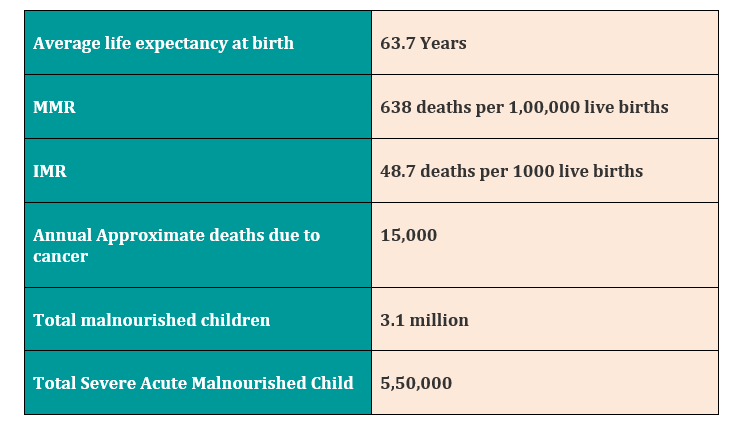
HEALTH INDICATORS
HEALTHCARE FINANCING
- Healthcare financing in Afghanistan primarily relies on government funding, social health insurance, community-based health insurance, private health insurance, and private out-of-pocket expenses.
- Afghanistan has a national health service managed by the Ministry of Public Health (MoPH) and financed by donors and the government. It provides health care services through two packages, BPHS and EPHS, which are fully subsidized by the government with the support of international donors.
- Out of Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) is the largest source of healthcare funding in Afghanistan, accounting for approximately 75% of the Total Health Expenditure (THE). Households often use and pay for private healthcare services, with 62% of OOP spending directed toward private facilities.
- Afghans spend an estimated $300 million a year on medical treatment abroad, mainly in Pakistan, India, and Turkey.
HEALTHCARE INFRASTRUCTURE
- Afghanistan’s healthcare infrastructure is limited, and there are few hospitals and clinics, especially in rural areas.
- Many healthcare facilities have been damaged or destroyed by years of conflict.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are only 0.3 hospital beds per 1,000 people in Afghanistan.
- The Ministry of Public Health of Afghanistan deals with matters concerning the healthof Afghanistan‘s population.
- There are 117 government-run or private or internationally-administered hospitals.
HEALTH WORKFORCE: 2023
- Physician: 11,400 per 1000 population
- Nurses: 20,000 (Approx.)
CURRENT HEALTHCARE SUPPORT SCENARIO FROM UNICEF IN AFGHANISTAN (2023)

MAJOR HOSPITALS IN AFGHANISTAN
Top Public Hospitals in Afghanistan
- Aliabad teaching hospital
It is one of the historical curative hospitals in the country and the world, its foundation stone with a capacity of 500 sick beds was put by Mohammad Nadersha on Aliabad mountain slopes in 1931. It has 12 different departments; such as general surgery, angina surgery, urology surgery, neurological surgery, orthopedic surgery, cardiology and respiratory section, endocrinology, hematology, Radiology, neurology, and mental disorder, internal digestive section, and with the presence of total 397 professional personals.
- Sardar Mohammad Dawood Khan Hospital
The Sardar Mohammad Daoud Khan National Military Hospital, often referred to as the Daoud Khan Military Hospital or the National Military Hospital, is a military hospital located in Kabul, Afghanistan. With 400 beds, it is the largest military medical facility in Afghanistan. It was constructed by the Soviets in 1973. The hospital was established to treat wounded Afghan soldiers and is funded largely by the United States federal government.[5] It is staffed entirely by Afghan doctors and nurses, with American military doctors and other U.S. personnel serving as mentors and advisors.
- Royal Medical Complex, Kabul
It is a multi-specialty accredited hospital under the Afghanistan Ministry of public health’s roles and Regulations. It was established in 2015 with a bed capacity of 100 beds. The thrust areas include Cardiology, Urology, and Plastic Reconstructive Surgery.
Top Private Hospitals in Afghanistan
- City Medical Complex, Kabul
It is a multi-specialty hospital that has made quality healthcare more convenient for communities throughout Afghanistan since 2016. It has a capacity of 517 beds. It has a broad range of services in many different medical, surgical, diagnostic, and rehabilitation specialties.
- Amiri Medical Complex, Kabul
It is a private hospital incorporated with the government of Afghanistan under the company’s ordinance 2015. The facility is located in the afghan red crescent, Afshar, area road in a green and calm environment suitable for the healthcare facility. It has a capacity of 90 beds. It has 40 critical beds, three operation theatres, and 15 departments. AMC is the first private hospital in the country that invested heavily in the healthcare domain and has substantially contributed to the healthcare system in many ways.
- Ariana Medical Complex
It was established in 2009 with a 50-bed capacity. It is a well-running and HI-tech hospital that is fully equipped with the latest and most modern state-of-the-art medical and surgical machinery.
- M. Mussa Wardak hospital
It was founded in 1991 with the approval of the Ministry of Public Health Republic of Afghanistan and is among the few corporate hospitals which provide world-class treatment to patients round the clock around Kabul City. It is one of the nation’s finest orthopedics programs, combining first-rate medical care, personalized attention, and innovative scientific research to provide the best possible treatment for patients.
Top internationally administered hospitals
- Boost hospital
It was established by Médecins Sans Frontières in partnership with the Ministry of Public Health, this hospital is one of the biggest Médecins Sans Frontières hospitals run worldwide. It has 300 beds, 700 national staff, and 25 international staff.
- The French Medical Institute for Mothers and Children, Kabul
It was established in 2006 through a partnership between the government of France and Afghanistan, this tertiary hospital is located in Kabul. It earned a name for conducting the first open-heart pediatric cardiac surgery in Afghanistan on a 13-year-old girl, at a very nominal amount. The hospital has 169 beds, which includes 15 intensive care beds for children.
- Indira Gandhi Children’s Hospital, Kabul
It is located in Kabul, this hospital is a children’s hospital with 150 beds. In 2004, it also began the first cerebral center with the help of the Indian government.
CONCLUSION
Afghanistan’s healthcare system faces numerous challenges, including inadequate funding, limited resources, and security concerns. The country heavily relies on international aid to provide basic healthcare services to its population, and the majority of healthcare expenses are paid out of pocket by households. While progress has been made in recent years, there is still a long way to go to provide adequate and accessible healthcare to all Afghans, particularly in remote and conflict-affected areas.
Above is the superficial and macro level study for in-depth market and financial feasibility studies or any other healthcare-related research needs, please feel free to reach out to us at +91-8655170700 or email us at hospaccx.india@gmail.com . Our team is equipped to provide comprehensive and detailed insights tailored to your specific requirements.
Related Team Members