Are you planning to build or restructure or venture into Cardiac Hospital in India? Looking for information about the major healthcare players in Government, Private diagnostic centers that are available in India? Are you looking to find out which part of the city is best to venture into or what all facilities are available and what should be planned for the new setup? In this article, Hospaccx Healthcare Consultancy has mapped all on major players in terms of Cardiac facilities and healthcare scenarios in India.
INTRODUCTION
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have now become the leading cause of mortality in India. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels, including coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, rheumatic heart disease, congenital heart disease, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. A quarter of all mortality is attributable to CVD. Ischemic heart disease and stroke are the predominant causes and are responsible for >80% of CVD deaths.
Individuals at risk of CVD may demonstrate raised blood pressure, glucose, and lipids as well as overweight and obesity. Identifying those at the highest risk of CVDs and ensuring they receive appropriate treatment can prevent premature deaths. Access to essential NCD medicines and basic health technologies in all primary healthcare facilities is essential to ensure that those in need receive treatment and counseling.
MARKET OVERVIEW OF CARDIOLOGY IN INDIA
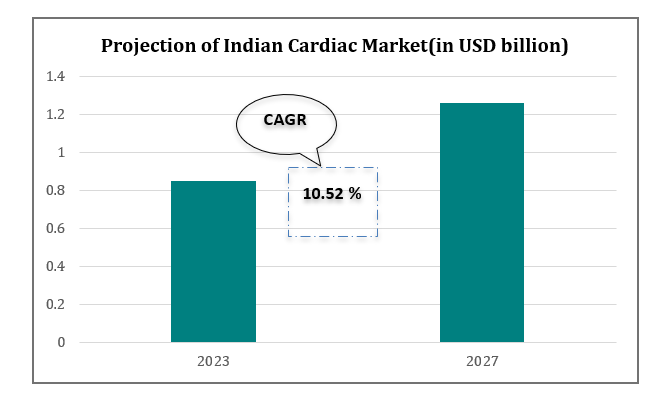
- Revenue in the Cardiology Devices segment in India is projected to reach US$0.85 bn in 2023.
- Revenue is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 10.52%, resulting in a market volume of US$1.26bn by 2027.
- The market is growing at a rapid pace due to the usage of advanced and latest devices in cardio rhythms such as pacemakers, defibrillators, implantable cardiovascular defibrillators, and cardio resynchronization therapy devices, which assist in the treatment of heart abnormalities, which boost the sales of Indian cardiology market.
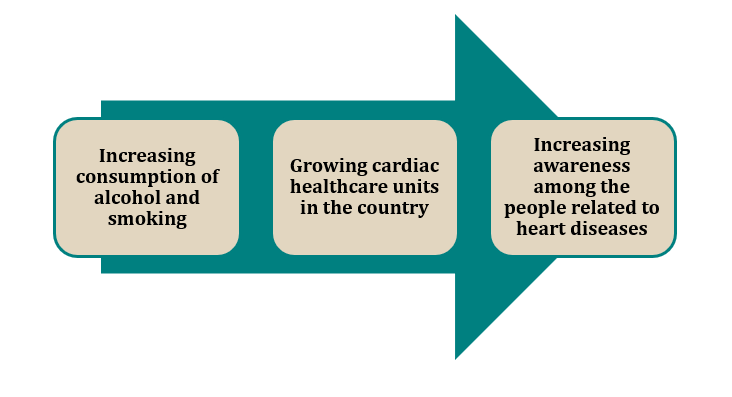
CARDIAC MARKET GROWTH DRIVERS IN INDIA
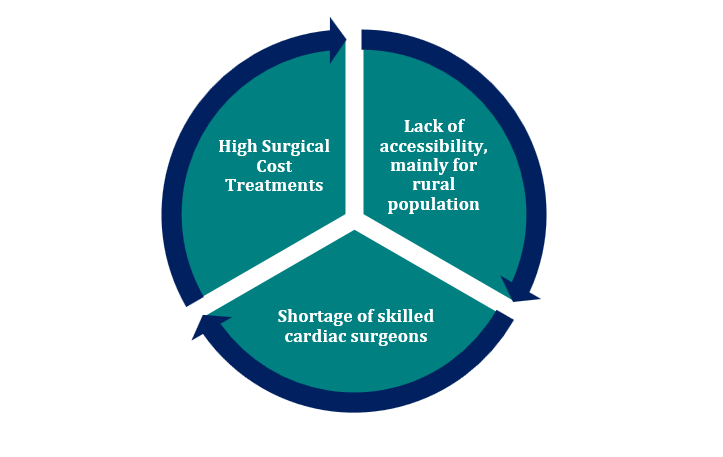
CARDIAC MARKET CHALLENGES IN INDIA
CARDIOLOGY INVENTIONS
- BARC develops credit card-size ECG machine that will cost around Rs 4,000
It is just slightly bigger than your debit or credit card and it is a full-fledged ECG machine. A team from Bhabha Atomic Research Centre has developed a compact ECG machine, which will also be pocket friendly. The researchers claim that people will be able to afford one of these machines for their private use, just the way they use a personal blood sugar monitor or blood pressure monitor.
Also, an app will connect the device to a smartphone and the user will not have to undergo any special training to operate this little wonder. The BARC team estimates that the machine dubbed Tele-ECG would be priced at around Rs 4,000. The commercial machines currently available in the market cost between Rs 40,000 and Rs 50,000.
- Indian innovation offers cheap and effective tests for heart disease
Scientists at the Healthcare Technology Innovation Centre (HTIC) in the southern Indian city of Chennai have invented a friendly device that keeps a check on artery stiffness and gives an alert when issues arise. The device, which is about the size of a digital television set-top box, has been tested in three different clinical trials. All tests found the Indian machine to be on par with the commonly used imaging system.
PREVALENCE OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE IN INDIA
- Cardiovascular diseases have been gaining importance in India recently because of the increased incidence of the disease. It is the first among the top 5 causes of death in the Indian population.
- In India, studies have reported increasing CHD prevalence over the last 60 years, from 1% to 9%-10% in urban populations and <1% to 4%-6% in rural populations.
- In the 30-74 age group, the overall 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease in women is 12.7%, as compared to 21.4% in men.
- CVD risk tended to be the highest in south India (including Goa), the three most northern states in the dataset (Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Uttarakhand), the north-eastern states (except Assam), and West Bengal (particularly among males).
- By 2030, almost 23.6 million will die from CVDs, mainly from heart disease and stroke.
GOVERNMENT POLICIES FOR CVDS
| National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS) (2010)
Aim: To prevent and control non-communicable diseases, including CVDs About: Carrie’s health promotion and screening, early diagnosis, and management of non-communicable diseases. |
| Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) (2018)
Aim: To provide free secondary and tertiary healthcare services to economically vulnerable citizens in India, making it the largest government-funded healthcare scheme in the world About: Under this scheme, eligible beneficiaries are provided with health insurance coverage of up to Rs. 5 lacks per family per year for the treatment of serious illnesses and medical conditions. |
| National Health Mission (NHM) (2005)
Aim: To improve the availability and accessibility of quality healthcare services in rural areas of India and reduce maternal and infant mortality rates About: This scheme aims to strengthen the primary healthcare system in rural areas by providing funds for the construction of new health facilities, hiring and training of healthcare workers, and implementation of various health programs and initiatives. |
| National Programme for Health Care of Elderly (NPHCE) (2010)
Aim: To provide accessible, affordable, and high-quality healthcare services to the elderly population of India About: The program focuses on preventive, promotive, curative, and rehabilitative aspects of healthcare for the elderly, and aims to provide integrated healthcare services through primary, secondary, and tertiary levels of healthcare delivery. |
| National Tobacco Control Program (NTCP) (2007)
Aim: To raise awareness about the harmful effects of tobacco use, and to reduce tobacco consumption in the country About: The program is implemented at both national and state levels and aims to work in collaboration with various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and community-based organizations. |
LIST OF MAJOR CARDIOLOGY HOSPITALS IN INDIA
Chain of major cardiology hospitals in India
- Narayana Hrudyalaya
Dr. Devi Shetty founded Narayana Hrudalaya (NH) in the year 2000 with a 280-bed heart hospital in Bangalore. The following is its chain of cardiac hospitals across India.
- MS Ramaiah Narayana Heart Centre, Bangalore (2007)
- Narayana Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Bangalore (2000)
- RL Jalappa Narayana Heart Centre, Kolar (2001)
- SDM Narayana Heart Centre, Dharwad (2008)
- SS Narayana Heart Centre, Davengere
- Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Kolkata (2000)
- Sona Cardiac Care
It is a chain of Speciality Cardiac Intervention Hospitals created for the sole purpose of treating people suffering from cardiac disease. It was established in 2012. Each hospital is a center of excellence in Non-invasive Cardiology, Coronary Interventions, and Cardio Thoracic and vascular surgery.
- Sona @ aims hospital, Pune (2012)
- Sona Nikop heart care centre, Satara (2015)
- Sona – Lokmanya cardiac center, Pune
- Sona rainbow cardiac care center, Agra
- Unicare heart institute and research center, Surat
- Meditrina Hospitals
It was established with its headquarters in Kollam in the state of Kerala. It is one of the top multi-specialty hospital chains in India engaged in providing primary as well as tertiary healthcare services. Its presence is in 11 locations across India, Maldives & Kenya.
Major cardiology hospitals in India
1. Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Delhi
It was established in 1988. At present capacity, the hospital has 285 beds along with 13 OTs, 158 ICU beds, 5 Cath Labs, 50 emergency beds, and an e-ICU facility. The hospital spans an area of 230,000 sq. ft. The hospital also has a Dual CT scan and a pacemaker clinic, an ICD clinic, and a heart failure clinic. The 3D echo facility at this hospital is of great help in diagnostics.
2. Asian Heart Institute, Mumbai
It was established in 2002. The hospital has a capacity of 250 beds. It spans an area of 1,50,000 sq. ft. The hospital has more modern OTs, equipped intensive-care beds, and ISO, and JCL accredited. The 80-bed ICU has the latest equipment like ventilators defibrillators, ECG, and Intra-aortic balloon pump. The ICU design at AHI has set a standard in the country. It has a 22-bedded cardiac ICCU (Intensive Coronary Care Unit) for round-the-clock care; 5-bedded Pre & Post cath beds, and 6 Bedded Surgical ICUs. It also comes under one of the top five cardiac hospitals in the country.
3. Narayana Institute of Cardiac Sciences
It was established in 2000. Narayana Health operates a chain of hospitals across India, with a focus on affordable and accessible healthcare. Narayana Health has several cardiac centers, including the Narayana Institute of Cardiac Sciences in Bangalore, which is a dedicated cardiac specialty hospital. It consists of 1000 Beds, 24 operation theatres, and infrastructure to perform 50 major heart surgeries daily.
4. Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences (RTIICS)
It is also popularly known as RN Tagore Hospital, Kolkata, it is a 681-bedded, NABH-accredited multi-super specialty quaternary care hospital, established in the year 2000. It is a unit of Narayana Health that focuses on cardiology services. RTIICS has 15 fully-equipped operation theatres and 4 state-of-the-art catheterization laboratories with 24-hour facilities.
5. Max Heart and Vascular Institute
It was established in 2001. Max Healthcare operates a chain of multi-specialty hospitals across India, with a focus on cardiology. Max Heart and Vascular Institute is a 225-bed state-of-the-art cardiovascular facility located in Saket, South Delhi. It has 43 critical care beds and 15 step-down beds. There are a total of 7 operation theatres available at the hospital, including 2 dedicated cardiac catheterization labs.
6. Metro Heart Institute, Faridabad
It was established in 2009, this is a dedicated cardiology center located in Faridabad, Haryana spanning over an area of 1,50,000 sq. ft. It has 150 beds, including 28 ICU beds, 4 OTs, and 8 emergency beds.
7. Sri Jayadeva Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences and Research
It is a government-run Autonomous Institute with 1150 Beds exclusively for Cardiac care and is one of the largest single centers for heart care destinations in South East Asia. It has got the State of the art equipment in the form of 7 Cath labs, 7 Operation Theatres, Non-Invasive Laboratories, and 24-hour ICU facilities.
CONCLUSION
The cardiac market scenario in India in 2023 is dynamic and evolving. The demand for cardiac products and services continues to rise due to several factors, including an aging population, lifestyle changes, and increasing awareness about heart health. However, challenges remain in the Indian cardiac market, including affordability and accessibility of advanced treatments, especially in rural areas. Health infrastructure and skilled healthcare professionals need further improvement to cater to the increasing burden of cardiovascular diseases. Government initiatives, collaborations between public and private sectors, and awareness campaigns are vital for addressing these challenges.
Overall, the cardiac market in India is poised for growth with an increased focus on innovation, preventive care, and patient-centric approaches. Continued advancements in technology, coupled with concerted efforts to improve healthcare infrastructure and affordability, will contribute to better cardiac care and outcomes in the country.
Above is the superficial and macro level study for in-depth market and financial feasibility studies or any other healthcare-related research needs, please feel free to reach out to us at +91-8655170700 or email us at hospaccx.india@gmail.com . Our team is equipped to provide comprehensive and detailed insights tailored to your specific requirements.
Related Team Members