INTRODUCTION
Accessibility of doctors’ offices, clinics, and other health care providers is essential in providing medical care to people with disabilities. Due to barriers, individuals with disabilities are less likely to get routine preventative medical care than people without disabilities.
Medical care providers are required to provide disabled individuals:
- Full and equal access to their health care services and facilities
- Reasonable modifications to policies, practices, and procedures when necessary to make health care services fully available
Considering the above facts, Hospaccx team participates in the market trends and dynamic of barrier free design. This is macroficial study of Barrier Free Design for Hospital if you want to get into more detail you can contact.
BARRIER FREE DESIGN FOR HOSPITAL
- Ramps and Stairs
There must be at least one entrance to the hospital, which has a ramp adjacent to the stairway leading inside the building. The inclination of the ramp is designed such that the slope isn’t too steep assuming the wheelchair bound people may enter without any assistance. Having large ramps inside the building occupies a lot of space and thus, other alternate provisions must be made. In absence of a ramp, the steps of the stairs can have wide levels keeping the space requirement for the wheels of a wheelchair in mind.
- Entrances, Exits and Passages
All entrances, exits and corridors/passages should be wide enough and designed such that wheelchair bound people travel with ease. All major entrances should use automatic doors that open when sensors detect someone approaching. The doors open by sliding to the side, rather than opening outward, to allow unobstructed access for people in wheelchairs and scooters. The grade of the slopes of ramps should be barely noticeable, making it easier for people in wheelchairs to propel themselves up and down the ramps.
- Hallways, Elevators and Wayfinding
Handrails are abundant throughout areas where patients travel. Braille alongside floor buttons and audio announcements of the floor location to accommodate people with visual disabilities. Primary overhead wayfinding signs should be in English and local language and in high contrast to enhance readability. Contrasting borders on the edges of hallway carpeting and around patient and procedure room doorways help patients with low vision navigate more easily. Furnishings in public areas, along with other features, accommodate bariatric or larger patients.
- 4. Flooring
It is important for the flooring to be of an anti-slip material for the safety of amputees and handicapped persons who require the support of canes and crutches.
- 5. Range of grasp
The knowledge of the ability and physical reach of people on wheelchair enables the design team to conveniently locate controls, switches and handles, etc. in patient populated rooms. Research shows that the forward reach of a physically challenged / wheelchair bound person in the upward direction is approx. 1220mm max and downward is approx. 380mm min.
- 6. Rooms and doors
In non-medical areas, doors can be of sliding type operated manually or automatically. The main entrance to the hospital is generally seen to have automatic sliding doors. In other areas, such as toilets, change rooms the door must open outwards. In patient rooms, the door preferably opens inwards.
- 7. Toilets
There must always be at least one handicap toilet on each floor of the hospital. The toilet bowl should preferably be a stool type. At least one of the toilet bowls must have a handrail installed. The door should, as a rule, be outward-opening. The door lock must be easily operable. Also, an indication must be provided on the outside of the stall to show that the toilet is occupied.
Such toilets must be easily accessible with special provisions of hand bars /support handles at all areas of use. Foldable handle bars can also be used for convenience, provided the folding mechanism is of very good quality so as to prevent any accidents.
- 8. Signage, layout diagrams
Universal signs need to be displayed to convey important information for e.g., caution near a step or at the beginning of the staircase, danger in electrical or waste disposition areas, etc. This signage must be incorporated in the mandatory signage that every hospital requires to have. Such signs can either be illuminated or of bright contrasting colors. Floor maps in multiple locations on every floor of the hospital, which is mandatory in every hospital today, will also help people with impaired hearing and who only rely on vision, during way finding. These maps form a precautionary measure for fire safety too.
- 9. Hand railings, Information boards, information in Braille
All ramps and staircases must have continuous hand railings. This is of utmost importance as it provides assistance not only to the disabled but also to the elderly. Information boards need to be displayed at each floor stating the location of each department indicating their directions as well as doctor’s information. Lifts, public telephones must also have denotations in braille. Information brochures could also be made available in braille too.
- 10. Parking Lot
If a hospital has ground level parking, certain blocks close to the entrances are to be designated for the handicapped. Such areas are demarcated with the handicap symbol in order to differentiate from the others.
- Treatment and Services
- Patient treatment carts in the Emergency Department are height-adjustable so they can be lowered as needed to better accommodate people in wheelchairs.
- New MRI machines can accommodate patients with unique spinal curvatures.
- Patient registration counters and electronic information signs are at a level that is accessible for people in wheelchairs.
- Patient Room
- All acute care and critical care adult patient rooms should be built-in ceiling tracks to accommodate lift devices for patients with disabilities. Patient phones have large numbers on the dial pad and volume controls to help people with visual or hearing impairments.
- Bathroom doors in acute care patient rooms swing in both directions, to enhance emergency access and to allow people in wheelchairs to enter and leave more easily. They also have a 5-foot-diameter turning radius to allow patients in wheelchairs to manoeuvre inside the room.
- In all patient rooms and bathrooms, handrails are provided between the patient bed and the bathroom, around the toilet and inside the shower so that patients can lift themselves up and ease themselves down. Showers have a fold-down seats for patients who cannot or prefer not to stand and have no raised border on the floor to ease patient access.
- Pivoting arms on patient recliner chairs in acute care and critical care rooms can be lifted up to allow better access to the patient.
- Whiteboards in each room allow staff members to write notes for patients with hearing disabilities, and all televisions in patient rooms have patient-controlled closed-captioning.
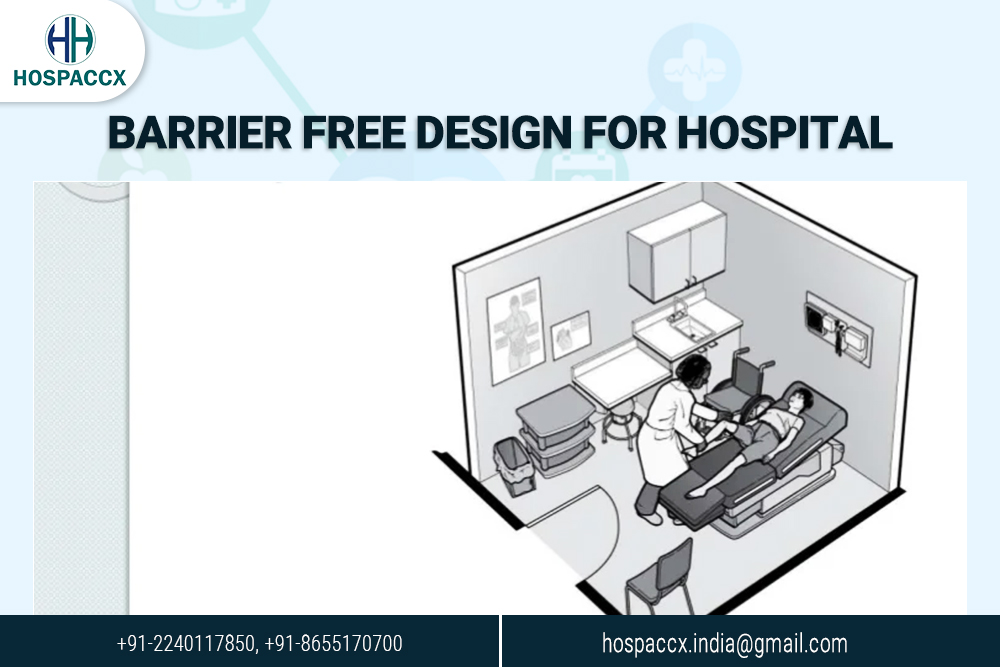
- Accessible Examination Rooms
The features that make this possible are:
- An accessible route to and through the room.
- An entry door with adequate clear width, manoeuvring clearance, and accessible hardware.
- Appropriate models and placement of accessible examination equipment.
- Adequate clear floor space inside the room for side transfers and use of lift equipment.
The number of examination rooms with accessible equipment needed by the medical care provider depends on the size of the practice, the patient population, and other factors.
- Ceiling Mounted Lifts
Ceiling structure must support weight of lift and person. Overhead track lifts can be used in rooms with limited floor space or where an exam table cannot accommodate a portable floor lift.
hospital architecture planning and design
CONCLUSION
The hospital layouts designed must be compatible to people with disabilities such as blindness/ low vision, locomotive disability: non-ambulatory, partial ambulatory; impaired hearing, etc. Efforts should be made in order to design/develop efficient barrier free paths for disables.
Are you planning to design your healthcare organisation? We can help you to design your dream project, below are the healthcare design services that we offer:-
- Healthcare Architecture Design services
- MEP Design
- Landscape Design services
- Structural Design services
- Interior Design services
It is the superficial and macro level study for more details kindly contact Hospaccx Healthcare business consulting Pvt. ltd on hospaccx.india@gmail.com Or you can visit our website on https://hospaccxconsulting.com
Related Team Members