Exploring Morocco’s healthcare landscape, this article, brought to you by Hospaccx Healthcare Consultancy, provides insights into the government’s healthcare initiatives, the presence of private medical facilities, and emerging investment opportunities. Whether you’re exploring development, restructuring, or investment prospects within Morocco’s healthcare sector, our analysis offers valuable information on the existing infrastructure and promising avenues for investment.
Introduction
Nestled in North Africa, Morocco’s diverse cultural heritage and stunning landscapes captivate visitors. Its capital city, Rabat, stands as a vibrant hub of culture and administration, reflecting the nation’s rich history and modern aspirations. Yet, beneath its surface lies a healthcare landscape grappling with a rising burden of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer. While strides have been made in reducing maternal and child mortality, challenges like tuberculosis persist. However, Morocco’s proactive approach to disease control, including successful immunization programs, and its leadership in HIV/AIDS management highlight its commitment to public health.
Demography
| Population | 37,840,044 (2023 est) |
| Population Density | 85 per Km2 (220 people per mi2) (2023 est) |
| Sex Ratio | 0.96 (961 male per 1,000 female) (2023 est) |
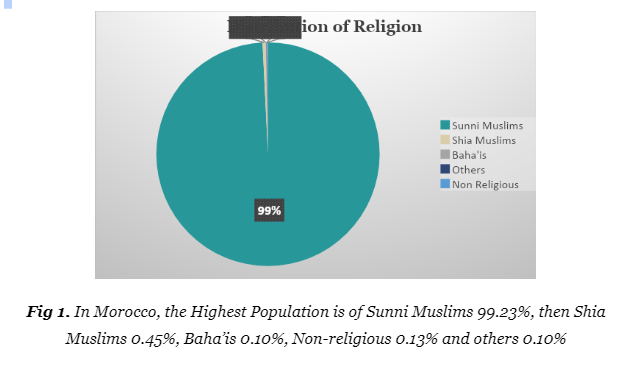
| Ethnicity | Arabs (44%), Arabized Berbers (24%), Berbers (21%), Beidane (10%), Others (1%) |
Economy
GDP Growth Rate:
- 2022: 1.3%
- 2023: 2.8%
- 2024 (Projected): 3.1%
Fiscal Deficit (%):
- 2022: 5.3%
Current Account Deficit (% of GDP):
- 2022: 3.2%
Agricultural contribution to GDP (%):
- 2022: 10.33%
Services contribution to GDP (%):
- 2022: 54.48%
Industry contribution to GDP (%):
- 2022: 25.48%
Main drivers of Growth:
- 2022: Agriculture, manufacturing, services, tourism
Some Important Health Statistics
- Total fertility rate – 2.3 live births per woman (2023 est)
- Infant Mortality rate – 13.7 deaths per 1,000 live births (2023 est)
- Urban Population – 65.9% (2023 est)
- Rural Population – 34.1% (2023 est)
- GDP growth rate – 2.8% (2023 est)
Major Diseases in Morocco
| Diseases | Description |
| Hepatitis A | Viral infection affecting the liver, spread through contaminated food or water. |
| Hepatitis E | Liver infection caused by contaminated drinking water. Symptoms include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and yellowing of the skin and eyes. |
| Typhoid Fever | Bacterial disease transmitted through contaminated food or water. Presents with fever, abdominal pain, headaches, and gastrointestinal issues. |
| Leishmaniasis | Infection transmitted by sandflies, posing a significant public health threat in Morocco. |
| Schistosomiasis | Waterborne disease caused by parasitic flatworms. Larvae penetrate the skin in contaminated water, leading to urinary or intestinal issues. |
| Malaria | Parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes. Symptoms include fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms. 90% of cases occur in sub-Saharan Africa. |
| Yellow Fever | Viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes, potentially causing severe hepatitis and hemorrhagic fever. |
Top 5 Causes of Mortality in Morocco
- Ischemic Heart disease – 38%
- Stroke – 22.5%
- Tuberculosis – 18%
- Injuries – 7%
- HIV/AIDS – 4%
In Morocco, ischemic heart disease and stroke stand out as the leading causes of mortality, together contributing to a significant portion of deaths. This is compounded by prevalent risk factors such as tobacco smoking, physical inactivity, hypertension, and depression. With challenges like illiteracy, poverty, and an underprepared healthcare system, these mortality rates are anticipated to rise in the coming years.
Healthcare Scenario in Morocco
- Proactive policies have been adopted to digitize the healthcare sector, aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- The government plans to extend digitalization efforts to all regions, implement IT programs for primary healthcare facilities, and introduce shared medical files.
- The overarching goal is to create a healthcare model based on solidarity and cohesion, with a focus on improving access for vulnerable populations, chronic illness patients, and the elderly.
- Significant budget increases demonstrate the government’s commitment to healthcare, ensuring adequate resources for an efficient national health system.
Healthcare Related Human Resources in Morocco
|
28,892 |
|
4,500 |
|
37,376 |
|
5,700 |
|
9,742 |
Major Medical Institutions in Morocco
PUBLIC
-
Ibn Tofail University Hospital – 1000 beds
A key healthcare institution in Marrakesh, Morocco, underwent major expansions in 2001 with support from The OPEC Fund for International Development. This included new construction, upgraded medical equipment, and rehabilitation of existing hospital space.
-
University Hospital Center Ibn Rochd, Casablanca – 37 beds
Formerly known as Maurice Gaud, Jules Colombani, and Jean Vial military hospitals, originated in the 1930s. Renamed Ibn Rochd Hospital in 1953, it integrated medical training programs in 1975, becoming the Ibn Rochd University Hospital Center.
-
Moulay Youssef Hospital – 250 beds
Moulay Youssef Hospital in Casablanca, Morocco, provides comprehensive healthcare services. They aim to enhance the performance of our operating room by addressing any existing weaknesses.
-
University Hospital, Tangier, Morocco – 800 beds
Features three interconnected buildings on a shared foundation, facilitating patient access and operational efficiency. A prominent awning extends from the entrance, creating a welcoming space for visitors and offering views of the city. Despite spatial constraints, the design ensures connectivity and functionality.
-
Centre Hospitalo-Universitaire Mohammed VI Marrakech, Morrocco – 325 beds
It is a leading-edge medical facility dedicated to research and education in medicine. It boasts modern amenities and 11 operating theaters meeting global standards. Specialized centers include the Mother-Child, Trauma, and Head and Neck Centers, providing efficient care in a conducive environment for staff development.
-
United Nations Clinic, Rabat, Morocco – 2,260 beds
The United Nations Clinic in Morocco, situated in Rabat, offers medico-surgical, obstetrical, and pediatric services to the community.
PRIVATE
-
Hospital Americain Internationale, Morocco – 700 beds
Stands as a pinnacle of excellence, offering cutting-edge diagnosis and treatment methods. With a team of expert medical professionals across diverse specialties, it boasts state-of-the-art facilities and technologies adhering to global standards.
-
Clinique Assalam Tangier, Morocco – 30 beds
Founded in 2007 by six Belgian-trained Moroccan doctors, is Tangier’s leading private clinic. It offers European-standard care in various specialties, with staff fluent in French and English to cater to the multilingual community.
-
Sheikh Zayed Hospital – 235 beds
Established in 1998, underwent modernization from 2008 to 2012, including a 20,000 m2 extension. Specializing in cardiology, vascular diseases, dental, plastic surgery, and other medical fields, it operates within the “hospitals and clinics” sector.
-
Clinique Internationale De Marrakech – 100 beds
Offers a range of facilities for international patients, including accommodation, airport transfers, meal choices, SIM cards, and in-room TV. The clinic also boasts modern infrastructure to support comprehensive medical care.
-
Anfa Fertility Center – 212 beds
Provides top-notch facilities and expert care for international patients, including accommodation, airport transfers, meal choices, interpreters, and more. With experienced doctors and high success rates, it’s a preferred choice for infertility treatment worldwide.
-
Clinique Averroes – 48 beds
Established in 1975 by Dr. Ahmed Laarbi Mansouri, it is a leading medical facility in Gueliz, Marrakesh. It offers specialized care in women’s health, obstetrics, gynecology, aesthetics, dental, imaging, and perinatal services. Equipped with four operating theaters and a skilled surgical team, the clinic provides advanced treatments with personalized attention.
-
Clinique Du Soleil, Marrakech, Morocco – 20 beds
Clinique Du Soleil, just 8 km from Marrakech Menara Airport, is accessible by taxi. Situated close to Marrakech’s historic sites like Marrakech Museum and El Badi Palace, patients have ample opportunities for sightseeing.
-
Mohammed VI University International Hospital – 260 beds
The contemporary Mohamed VI International University Hospital in Bouskoura, near Casablanca, integrates cutting-edge technology. Positioned conveniently near the highway, it provides top-tier treatment, surgery, and hospitalization services.
-
Private Hospital of Casablanca, Morocco – 220 beds
A multidisciplinary medical facility aimed at addressing the diverse medical and surgical needs of patients from various specialties and backgrounds. It prioritizes service quality through an excellence-driven approach.
Diagnostic Centre in Morocco
- Centre De Diagnostic Polyvalent, Taourirt, Morocco
- Metec Diagnostic sarl, Casablanca, Morocco
- Centre De Diagnostic, Bouarfa, Morocco
- Centre Diagnostic Polyvalent, Agadir, Morocco
- BMD (Biomedical Diagnostic), Casablanca, Morocco
- Center De Diagnostique, Marrakesh, Morocco
Conclusion
In Morocco, the healthcare sector is rapidly evolving, with a mix of public and private facilities offering a wide range of services. Major hospitals like Ibn Tofail University Hospital and Cheikh Zaîd Rabat Hospital, along with clinics such as Clinique Internationale Marrakech, provide advanced medical care. Government initiatives, including digitalization and universal health insurance, aim to enhance accessibility and quality. Despite challenges, Morocco is making significant progress in improving healthcare outcomes.
For more details on planning and designing healthcare facilities in Morocco, contact Hospaccx Healthcare Business Consulting Pvt. Ltd. Reach out to us via email at hospaccx.india@gmail.com or visit our website www.hospaccxconsulting.com. We are committed to supporting your healthcare endeavors in Morocco.
Related Team Members